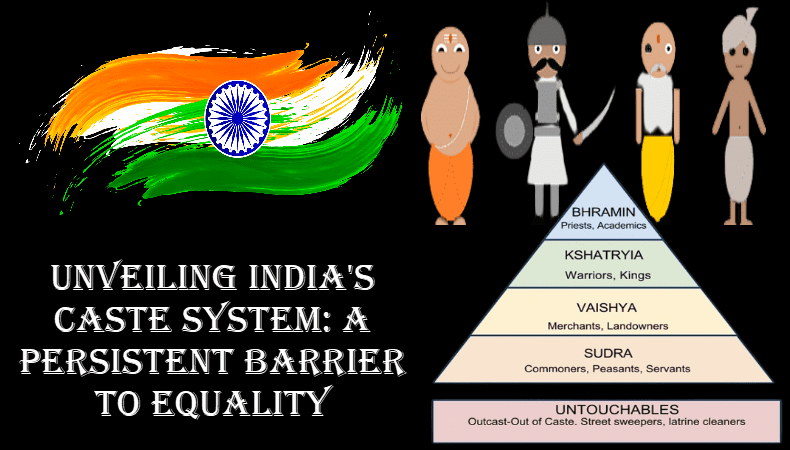
Caste is a complex social hierarchy in India that’s been around for centuries. Castes are believed to have originated in ancient India as a way to organize society by occupation and birth. There are specific duties and responsibilities for each caste in the Hindu religion. Brahmins were traditionally priests and scholars, while the lower castes did manual labor and menial tasks. Although the caste system has been abolished by the Indian constitution, it still exists in society and discriminates against people. It makes it difficult for marginalized communities to obtain an education, employment, and political representation.
Even though the caste system has been abolished, it continues to be a divisive issue in Indian society. Many people still live by it and it’s deeply ingrained in their culture. Caste still plays a big role in discrimination and oppression, especially for lower castes. Discrimination in the workplace, education, and politics is a great example of this. It’s also a major source of social tension and division, with violence and discrimination against marginalized communities still happening. The Republic Day celebrations in India serve as a reminder of the persistence of caste-based discrimination and the need for continued efforts to dismantle the system and promote equality and inclusion in Indian society.
“Religion is for man and not man for religion. For getting human treatment, convert yourselves. Convert to getting organized. Convert to becoming strong. Convert to securing equality. Convert to getting Liberty.”
~ B.R Ambedkar
The purpose of this article is to explain how the caste system perpetuates discrimination and inequality in India. We’ll also talk about how the Indian government, media, and society perpetuate or challenge the caste system, and provide examples of successful efforts to challenge and dismantle it.
Origins of the Caste system in India
Castes in India have their roots in ancient India when society was organized by occupation and birth into different classes. The caste system has its roots in Hinduism, with each caste having its own duties and responsibilities. Brahmins were traditionally priests and scholars, while lower castes did manual labor and menial tasks. Each person fulfilled a specific role based on their caste as a way to maintain order and stability in society.
Over time, castes became more rigid and hierarchical, with higher castes enjoying more power and privileges. Caste was further reinforced by the British colonial government, which used it to divide and rule Indians. While caste was officially abolished by the Indian constitution after independence, it’s still a divisive issue in Indian society today.
Many people’s lives are influenced by the caste system, which is deeply ingrained in the culture. Especially for the lower castes, it’s still used for discrimination and oppression. Violence and discrimination against marginalized communities continue to be reported because of the caste system. Religion and social factors can contribute to the persistence of the caste system, including lack of education and awareness, cultural norms, and the government’s failure to dismantle it.
Current Scenario of Caste System
In India, the caste system persists and has a lasting impact on social, economic, and political life. Although the caste system was officially abolished by the Indian constitution, it’s still a divisive issue in Indian society. People in lower castes are still discriminated against and oppressed by the caste system.
Socially, the caste system perpetuates discrimination and marginalization, resulting in less opportunity and access to resources for certain communities. It includes education, healthcare, job opportunities, and political representation. People from lower castes often don’t have access to quality education, which leads to poverty and marginalization.
People from lower castes are often relegated to menial jobs and denied access to higher-paying jobs because of the caste system. The result is a lack of economic mobility and a cycle of poverty and marginalization for lower castes. Despite the efforts of the government to address this issue through policies and affirmative action, the caste system continues to be a major barrier to achieving true equality and inclusion in Indian society.
How does the Caste system Perpetuate Discrimination and Inequality in India?
There are a number of ways in which the caste system perpetuates discrimination and inequality in India.
- It creates a hierarchy of social classes, with higher castes enjoying greater privileges and power, while lower castes are marginalized and oppressed. As a result, marginalized communities lack equal opportunities and resources.
- Each caste is assigned specific duties and responsibilities in the Hindu religion. As a consequence, a rigid and inflexible social structure is created, with little room for upward mobility. Because of this, people from lower castes are often relegated to menial jobs and denied access to higher-paying occupations, perpetuating poverty and marginalization.
- Higher castes use the caste system to maintain their power and control. This has resulted in further marginalization and discrimination of those in lower castes due to a lack of representation and political power. Several examples of this can be seen in the ongoing issues of discrimination in the workplace, in education, and in politics
- The caste system has a significant cultural impact, leading to low self-esteem and self-worth among certain castes. This can result in mental health problems and perpetuate poverty and marginalization.
The caste system perpetuates discrimination and inequality in India in a number of ways, with a significant impact on marginalized communities. It creates a rigid social structure that leads to a lack of equal opportunities and access to resources, perpetuates poverty and marginalization, and is used as a means of maintaining power and control.
Role of the Indian government, Media, and society in perpetuating the Caste system
Several factors contribute to perpetuating or challenging India’s caste system, including the government, the media, and society at large.
Although the Indian government needs to enforce laws and policies that promote equality and inclusion, the implementation of these policies has been inconsistent and often ineffective. However, affirmative action policies, like reservations for marginalized communities in education and government jobs, haven’t addressed the root causes of discrimination and inequality. The government has also been criticized for not doing enough to stop caste-based violence and discrimination.
There’s also a role for the media in perpetuating or challenging caste systems. The media often perpetuates stereotypes and reinforces the caste system. Media coverage of caste-based discrimination and violence is often inadequate, focusing instead on sensational aspects of the story and failing to address the root causes.
The caste system is also perpetuated or challenged by society. The caste system is often reinforced by cultural norms and stereotypes, with certain castes stigmatized and discriminated against. Discrimination and inequality are often perpetuated by social attitudes toward marginalized communities.
The caste system in India has been challenged and dismantled by civil society groups, activists, and individuals. This includes raising awareness about the caste system and advocating for policies and laws that promote equality. Furthermore, grassroots movements and community-based organizations are working to empower marginalized communities.
Successful efforts to dismantle the Caste system
There have been several successful efforts to challenge and dismantle the caste system both within India and internationally.
In India, the government has implemented affirmative action policies, such as reservations for marginalized communities in education and government jobs. This has helped to increase representation and access to resources for marginalized communities. Additionally, the Indian judiciary has played an important role in challenging the caste system by interpreting the Indian Constitution in ways that protect the rights of marginalized communities and provide remedies for caste-based discrimination.
Civil society organizations and activists have also played a critical role in challenging the caste system in India. For example, the Dalit Indian Chamber of Commerce and Industry (DICCI) has been working to empower Dalit entrepreneurs and promote their economic and social rights. Additionally, many grassroots movements and community-based organizations have been working to empower marginalized communities and promote their rights.
Internationally, the United Nations and other international organizations have been working to challenge the caste system. The UN has passed several resolutions condemning caste-based discrimination and calling for the elimination of the caste system. Additionally, many human rights organizations have been working to raise awareness about the impact of the caste system and advocate for the rights of marginalized communities.
As individuals, we can take action by educating ourselves about the caste system and its impact, supporting anti-caste organizations, and speaking out against discrimination in our own communities. Let’s work together to dismantle the caste system and build a more equitable society for all.