New Insights into Jupiter’s Cloud Composition
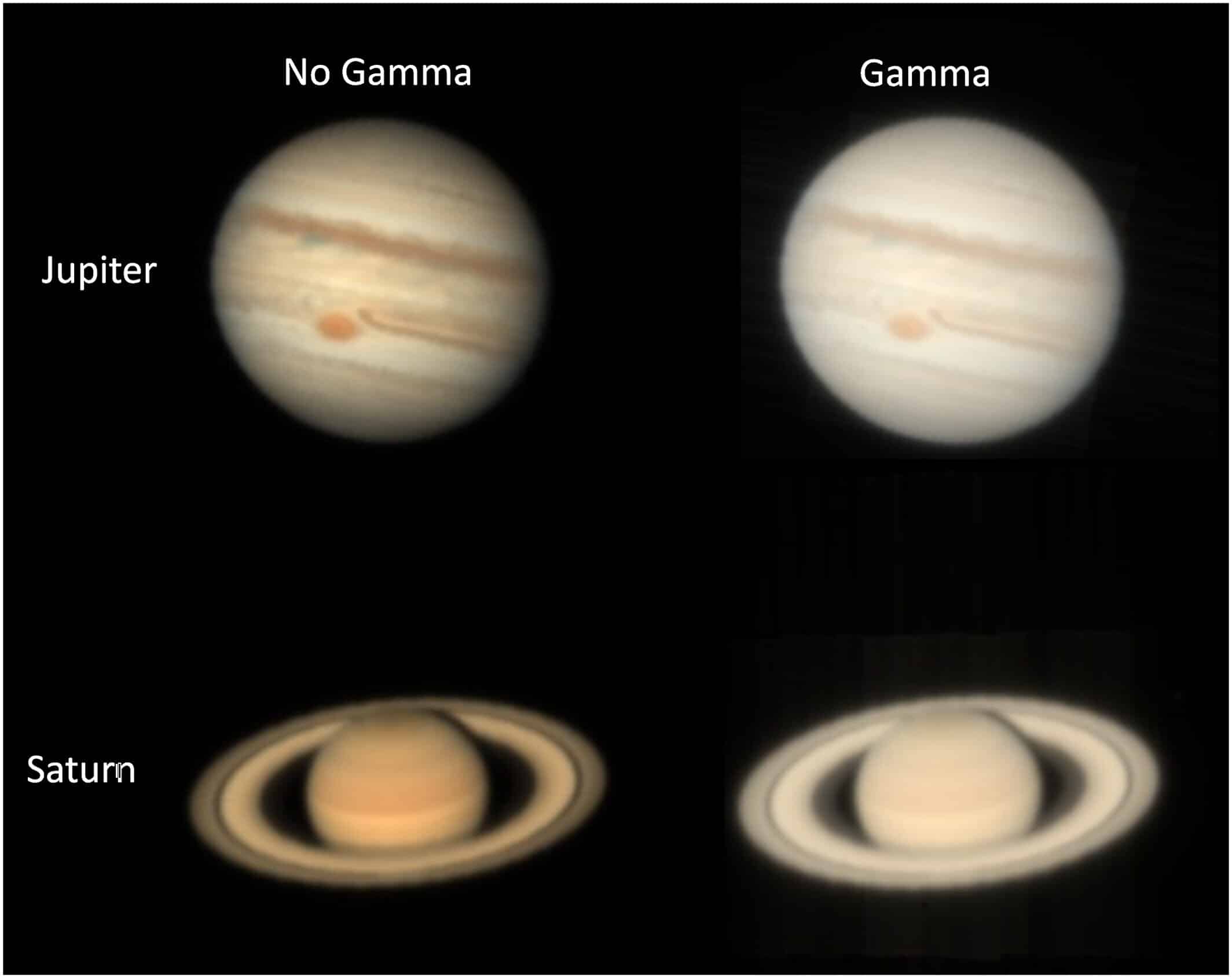
Recent discoveries have transformed our understanding of Jupiter’s clouds. Traditionally, scientists believed these clouds were primarily made of ammonia ice. However, new research indicates that they are actually composed of ammonium hydrosulfide mixed with photochemical materials. This groundbreaking revelation emerged from a collaboration between professional and amateur astronomers. It provides fresh insights into the composition and dynamics of Jupiter’s atmosphere. Moreover, it offers simpler methods for mapping the planet’s cloud layers, enhancing our ability to study this giant gas planet.
Ammonium Hydrosulfide Identified as Main Cloud Component
A significant breakthrough in understanding Jupiter’s clouds was published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. The study was led by amateur astronomer Dr. Steven Hill, who developed a novel method using commercial telescopes and specific filters. This technique allowed him to measure ammonia abundance and cloud-top pressures effectively. His findings revealed that Jupiter’s clouds exist in warmer regions of the atmosphere, deeper than previously thought. This was a surprising discovery, as scientists had long assumed that ammonia clouds were situated at higher altitudes.
Dr. Hill’s method was validated when applied to data from the Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE) instrument on the Very Large Telescope in Chile. Professor Patrick Irwin from the University of Oxford explained that simulations showed light interacting with gases at higher pressures and temperatures. This interaction ruled out ammonia ice as the primary component of the clouds. Instead, the research pointed to ammonium hydrosulfide mixed with smog-like materials. These substances are believed to contribute to Jupiter’s distinctive red and brown colors. This new understanding of cloud composition is crucial for future studies of Jupiter’s atmosphere and its weather patterns.
New Opportunities for Citizen Science
The study also highlights exciting opportunities for citizen scientists. Dr. Hill’s method, which compares brightness levels in narrow color filters, proved to be as accurate as more complex computational techniques. John Rogers from the British Astronomical Association noted that this simpler approach allows amateur astronomers to monitor Jupiter’s atmospheric features more frequently. By doing so, they can link chemical changes to observable weather phenomena, such as storms and the Great Red Spot.
This development is significant because it empowers amateur astronomers to contribute to scientific research. They can now observe and document variations in Jupiter’s atmosphere, providing valuable data that can enhance our understanding of the planet. Additionally, the study suggests that photochemical reactions in Jupiter’s atmosphere may prevent ammonia from condensing into clouds. Similar observations have been made on Saturn, indicating that photochemical processes play a crucial role in shaping the atmospheres of gas giants. This research opens new avenues for exploration and collaboration between professional and amateur astronomers.
Implications for Future Research
The findings about Jupiter’s cloud composition have far-reaching implications for future research. Understanding the true nature of Jupiter’s clouds can help scientists develop better models of the planet’s atmosphere. These models are essential for predicting weather patterns and understanding the dynamics of gas giants. The discovery that ammonium hydrosulfide plays a significant role in cloud formation challenges previous assumptions and encourages further investigation into the chemical processes at work in Jupiter’s atmosphere.
Moreover, this research can inform studies of other gas giants in our solar system and beyond. By applying the techniques developed by Dr. Hill, astronomers can explore the atmospheres of exoplanets and gain insights into their compositions. This could lead to a deeper understanding of how different planetary atmospheres evolve and behave. As technology advances, the collaboration between professional and amateur astronomers will likely continue to yield valuable discoveries, enhancing our knowledge of the universe.
Observer Voice is the one stop site for National, International news, Sports, Editor’s Choice, Art/culture contents, Quotes and much more. We also cover historical contents. Historical contents includes World History, Indian History, and what happened today. The website also covers Entertainment across the India and World.

