Innovative System Converts CO2 into Edible Protein
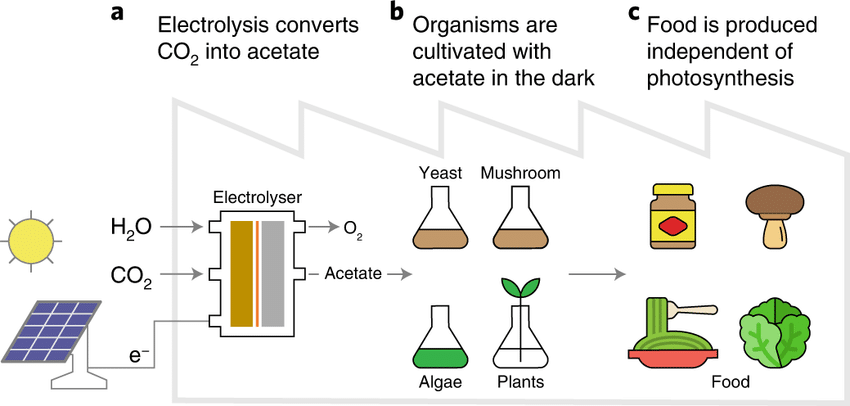
In a groundbreaking development, a team of engineers in China has created a system that transforms carbon dioxide into edible protein. This innovative dual-reactor technology addresses two significant global challenges: the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions and the growing demand for sustainable food production. As the world grapples with climate change and food insecurity, this system offers a promising solution. By converting CO2 from the atmosphere into a high-protein product, it aims to feed a burgeoning population while simultaneously tackling the environmental issues posed by greenhouse gases.
How the Dual-Reactor System Works
The dual-reactor system operates through a two-stage process, as detailed in a study published in *Environmental Science and Ecotechnology*. In the first stage, the system employs microbial electrosynthesis to convert carbon dioxide into acetate. This acetate serves as a vital intermediary in the process. Once produced, the acetate is transferred to a secondary reactor. Here, aerobic bacteria utilize the acetate to generate single-cell protein, which is suitable for both human and animal consumption.
This two-step method is not only efficient but also innovative. The use of microbial electrosynthesis allows for the direct conversion of CO2, a greenhouse gas, into a useful product. The design of the dual-reactor system ensures that the process is streamlined and effective. By focusing on the conversion of waste CO2 into a valuable food source, this technology represents a significant advancement in both environmental science and food technology. The ability to produce protein from CO2 could revolutionize how we think about food production and sustainability.
Efficiency and Nutritional Value
The efficiency of this dual-reactor system is noteworthy. According to the study, it achieved an impressive efficiency rate of 17.4 grams per liter of dry cell weight. The resulting protein boasts a concentration of 74 percent, which is significantly higher than the protein levels found in traditional sources like soybean and fish meal. This high nutritional value makes the protein produced by this system a viable alternative for both human food and animal feed.
The implications of this efficiency are profound. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for protein sources is increasing. Traditional methods of protein production often involve significant environmental costs, including land use and greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, this innovative system not only provides a high-quality protein source but does so while actively reducing atmospheric CO2 levels. This dual benefit positions the technology as a potential game-changer in the quest for sustainable food sources.
Cost-Effectiveness and Sustainability
Cost-effectiveness is a crucial factor in the viability of any new technology. The researchers behind this dual-reactor system have highlighted its minimal pH adjustments during the process. This feature reduces operational complexity and associated costs, making the system more accessible for widespread adoption. Furthermore, the system generates significantly less wastewater compared to conventional protein production methods. This reduction in waste contributes to a cleaner and more sustainable production process.
The economic advantages of this system could make it an attractive option for food producers. As sustainability becomes increasingly important to consumers and businesses alike, technologies that offer both environmental benefits and cost savings will likely gain traction. The dual-reactor system not only meets these criteria but also aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and promote sustainable practices in food production.
Implications for Future Food Security
The implications of this dual-reactor technology extend far beyond its immediate benefits. The research team suggests that this innovative approach could play a significant role in meeting global food demands. As the world faces the dual challenges of climate change and food insecurity, solutions like this one are essential. By providing a sustainable method for producing protein while actively reducing atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, this technology marks a significant step forward in addressing two critical issues of our time.
As countries strive to achieve food security for their populations, the adoption of such technologies could be pivotal. The ability to produce protein from CO2 not only addresses nutritional needs but also contributes to environmental sustainability. This dual benefit positions the dual-reactor system as a promising solution for the future of food production. As research continues and the technology matures, it may pave the way for a new era of sustainable food systems that prioritize both human health and the health of our planet.
Observer Voice is the one stop site for National, International news, Sports, Editor’s Choice, Art/culture contents, Quotes and much more. We also cover historical contents. Historical contents includes World History, Indian History, and what happened today. The website also covers Entertainment across the India and World.

