India’s Export Growth: A Record-Breaking Surge
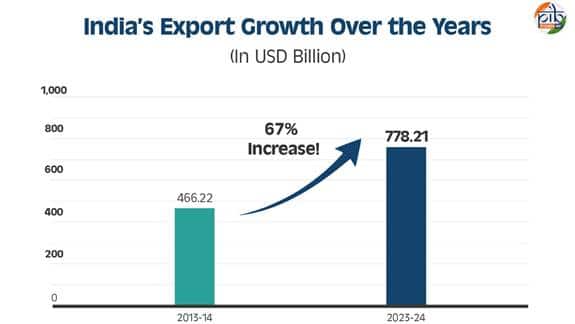
India’s export sector has achieved remarkable growth, reaching a staggering USD 778.21 billion in the fiscal year 2023-24. This figure represents a significant 67% increase from USD 466.22 billion recorded in 2013-14. The surge in exports highlights India’s expanding role in global trade, driven by robust performances in both merchandise and services. In 2023-24, merchandise exports accounted for USD 437.10 billion, while services exports contributed USD 341.11 billion. This balanced growth showcases the strength of key sectors such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, engineering goods, iron ore, and textiles. The growth trajectory has been bolstered by strategic policy measures, enhanced competitiveness, and improved market access. As a result, India’s export ecosystem is now more resilient and integrated into the global economy.
The momentum has continued into the fiscal year 2024-25, with cumulative exports from April to December 2024 estimated at USD 602.64 billion. This marks a 6.03% increase from USD 568.36 billion during the same period in 2023. The ongoing growth reflects the effectiveness of government initiatives and the adaptability of Indian exporters in a rapidly changing global market.
Export Classification and Growth Trends
India’s export landscape has evolved significantly over the past decade. Merchandise exports have surged from USD 314 billion in 2013-14 to USD 437.10 billion in 2023-24. This growth is primarily driven by a stronger manufacturing base and increased global demand for Indian products. Key sectors such as electronics, textiles, and engineering goods have played a pivotal role in this expansion.
In the same period, service exports have also seen impressive growth, rising from USD 152 billion in 2013-14 to USD 341.11 billion in 2023-24. The rise of information technology, financial services, and business services has fueled this growth. The diversification of export categories has strengthened India’s position in the global market.
The Indian government has implemented various policies to support this growth. Initiatives such as the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes and the National Logistics Policy aim to enhance manufacturing capabilities and reduce logistics costs. These measures have created a conducive environment for exporters, enabling them to tap into new markets and expand their reach.
Leading Export Regions Over the Years
India’s export destinations have diversified significantly over the years. In 2004-05, major export markets included North America, the European Union, North-East Asia, and the Gulf Cooperation Council. By 2013-14, these regions saw a marked increase in export values, with North America and the EU leading the charge. Fast forward to 2023-24, and North America has emerged as the largest destination for Indian exports.
The top merchandise export destinations in 2023-24 included the USA (17.90%), UAE (8.23%), Netherlands (5.16%), and China (3.85%). Together, these ten countries accounted for 51% of India’s total merchandise export value. This diversification reflects India’s efforts to strengthen trade relationships across various regions, enhancing its global trade footprint.
The growth in exports to these regions is a testament to India’s competitive advantage in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, textiles, and engineering goods. The government’s focus on improving trade relations and market access has further facilitated this expansion. As India continues to explore new markets, its export landscape is expected to evolve, creating more opportunities for growth.
Key Government Initiatives to Strengthen India’s Export Landscape
The Indian government has introduced several initiatives to bolster the export sector. The New Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2023 focuses on export incentives and ease of doing business. It aims to support emerging sectors like e-commerce and high-tech products. The policy also includes a one-time Amnesty Scheme to help exporters clear pending authorizations.
Additionally, the Interest Equalisation Scheme (IES) has been extended until August 31, 2024, with a substantial allocation to provide concessional interest rates on export credit. The RoDTEP and RoSCTL schemes offer tax and duty reimbursements to exporters, benefiting sectors like pharmaceuticals and chemicals.
Infrastructure development is another key focus area. The National Logistics Policy and PM GatiShakti aim to reduce logistics costs and enhance multimodal connectivity. The Production-Linked Incentive schemes promote large-scale manufacturing, further boosting exports.
Moreover, the government is working to improve the ease of doing business. Compliance reforms have reduced over 42,000 compliances, simplifying business processes. The National Single Window System streamlines approvals, allowing businesses to apply for multiple central approvals in one go.
Observer Voice is the one stop site for National, International news, Sports, Editor’s Choice, Art/culture contents, Quotes and much more. We also cover historical contents. Historical contents includes World History, Indian History, and what happened today. The website also covers Entertainment across the India and World.

