Empowering Farmers: The CGS-NPF Initiative
Introduction to the CGS-NPF Scheme
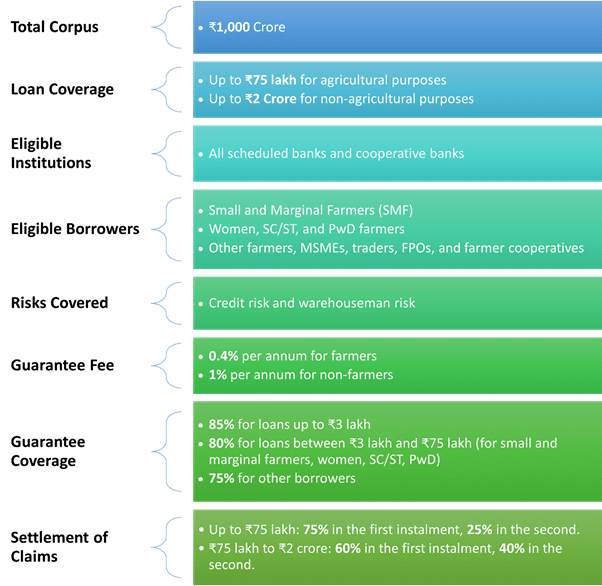
On December 16, 2024, the Government of India launched the Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR Based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF). This initiative aims to provide a ₹1,000-crore corpus to support post-harvest financing for farmers. The scheme allows farmers to access credit by pledging their produce stored in accredited warehouses. These warehouses are recognized by the Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority (WDRA) and utilize electronic negotiable warehouse receipts (e-NWRs). The primary goal of this scheme is to reduce distress sales among farmers, addressing a significant gap in agricultural finance.
The CGS-NPF initiative also encourages the registration and development of warehouses closer to farmland. This is crucial for improving the accessibility of storage facilities for farmers. Union Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution, Shri Pralhad Joshi, has urged the WDRA to expand its reach and ensure more warehouses receive accreditation. This expansion is vital for the success of the scheme and for enhancing the financial stability of farmers across India.
The CGS-NPF scheme aligns with the government’s broader efforts to strengthen Indian agriculture. Agriculture contributes 17.7% to the overall Gross Value Added (GVA) in FY 24 and employs nearly half of the population. Recognizing its importance, the government continues to prioritize initiatives that enhance productivity, provide financial support, and promote self-reliance among farmers. The CGS-NPF scheme is a significant step towards empowering farmers and fortifying the foundation of Aatmanirbhar Bharat.
Overview of the CGS-NPF Scheme
The Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR Based Pledge Financing has generated considerable interest from various stakeholders, particularly in the banking sector. By increasing post-harvest lending against e-NWRs, the scheme aims to improve farmers’ income and enhance their access to institutional credit. This is especially important for small and marginal farmers, who often struggle to secure loans due to a lack of collateral.
The scheme is designed with inclusivity in mind. It primarily benefits small and marginal farmers, women, Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST), and Divyangjan (PwD) farmers. These groups face unique challenges in accessing financial resources. The CGS-NPF scheme offers a minimal guarantee fee, making it more accessible for these vulnerable populations. Additionally, the scheme extends its advantages to small traders, Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs), and farmer cooperatives.
One of the key features of the CGS-NPF scheme is its focus on providing higher guarantee coverage for smaller loans. This approach supports equitable financial access, ensuring that even the smallest farmers can benefit from the scheme. By facilitating easier access to credit, the CGS-NPF scheme aims to empower farmers, improve their livelihoods, and contribute to the overall growth of the agricultural sector.
Key Agricultural Credit and Financial Support Schemes
In addition to the CGS-NPF scheme, the Indian government has implemented several other key agricultural credit and financial support schemes. One notable initiative is the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme, introduced in 1998. The KCC scheme provides farmers with easy access to agricultural inputs and cash for their production needs. In February 2019, the Reserve Bank of India extended the KCC facility to include Animal Husbandry and Fisheries, further broadening its scope. As of March 31, 2024, there are approximately 7.75 crore operative KCC accounts, highlighting its widespread adoption among farmers.
Another significant initiative is the Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS). This scheme offers concessional short-term agri-loans to farmers for crop and allied activities. Under MISS, farmers can access loans up to ₹3.00 lakh at a 7% interest rate. Additionally, there is an extra 3% subvention for timely repayment, effectively reducing the interest rate to 4%. The scheme also includes post-harvest loans against negotiable warehouse receipts for small farmers with KCCs. Since 2014-15, institutional credit flow to agriculture has nearly tripled, showcasing the success of these initiatives in enhancing financial support for farmers.
A Step Towards Agricultural Resilience
The launch of the Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR Based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF) marks a pivotal initiative aimed at enhancing post-harvest financing and reducing distress sales for farmers. With a ₹1,000-crore corpus, this scheme addresses a critical gap in agricultural finance by providing greater access to credit for small and marginal farmers, women, and Scheduled Castes and Tribes.
The CGS-NPF scheme complements the government’s broader agricultural support framework, which includes other key initiatives like the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) and the Modified Interest Subvention Scheme (MISS). Together, these schemes empower farmers, boost agricultural productivity, and promote self-reliance, thereby strengthening the foundation of Aatmanirbhar Bharat. As more farmers benefit from these initiatives, the vision of a resilient and self-sustaining agricultural sector in India becomes increasingly achievable. The government’s commitment to enhancing financial support for farmers is a crucial step towards ensuring their welfare and the overall growth of the agricultural sector.
Observer Voice is the one stop site for National, International news, Sports, Editor’s Choice, Art/culture contents, Quotes and much more. We also cover historical contents. Historical contents includes World History, Indian History, and what happened today. The website also covers Entertainment across the India and World.

