Donald Trump’s Tariffs: Implications for Key Manufacturing Sectors
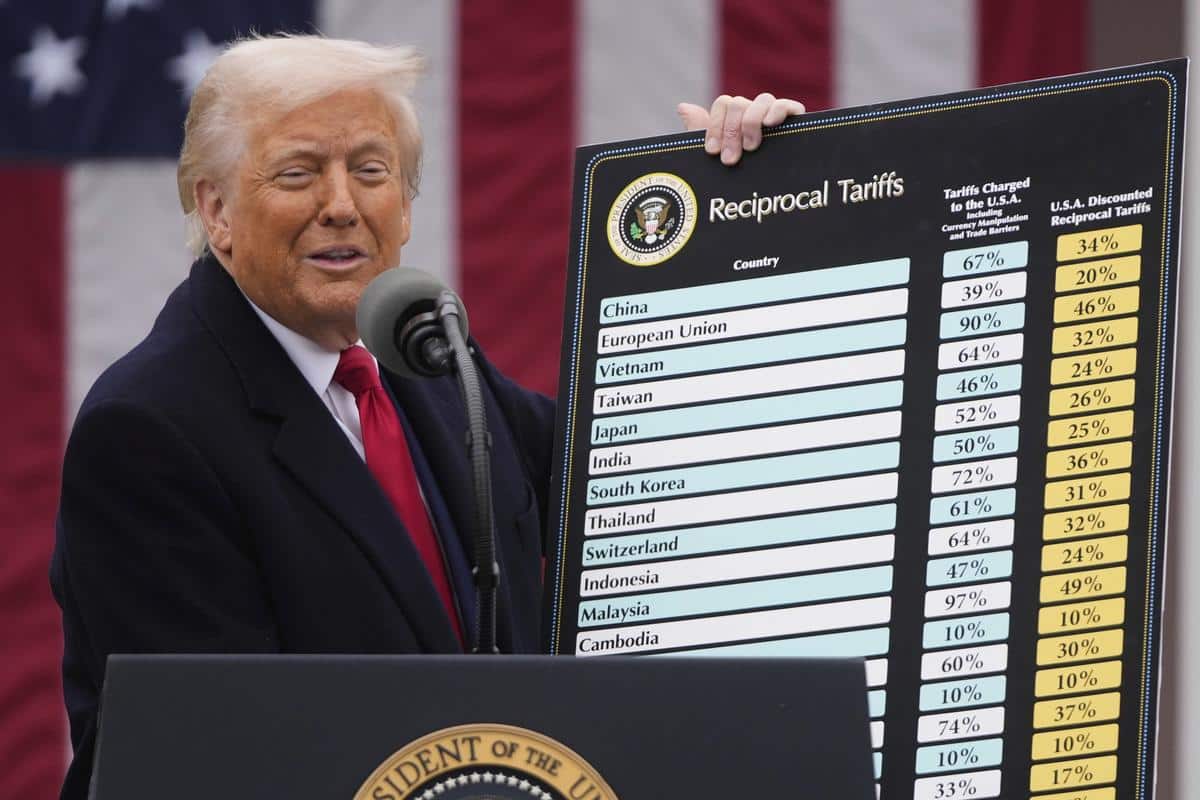
The United States has announced a 90-day suspension of higher reciprocal tariffs on its trading partners, a significant policy shift that occurred shortly after the tariffs took effect. This pause signals a potential easing of the tariff strategy amid ongoing trade negotiations. While the universal 10% base tariff on all imports remains, the U.S. has raised tariffs on Chinese goods to 125%, citing China’s retaliatory measures. This situation presents a unique opportunity for India to enhance its role as a key trading partner, particularly as global businesses seek alternatives to China.
Impact on Global Trade Dynamics
The recent decision by the U.S. to pause reciprocal tariffs could reshape global trade dynamics significantly. The suspension allows for potential diplomatic engagement and negotiations for trade agreements, particularly with India. As the U.S. continues to impose high tariffs on Chinese imports, American companies are compelled to seek alternative suppliers. This shift opens the door for India to position itself as a viable alternative, especially in sectors like electronics, where India has the potential to increase its exports and attract foreign investments.
The ongoing trade conflicts with China have created a favorable environment for India to enhance its manufacturing capabilities. As global businesses look to diversify their supply chains, India can capitalize on this trend by boosting its exports and improving its market access to the U.S. The temporary suspension of tariffs provides India with a unique window to strengthen its bilateral relations with the U.S. and work towards a more favorable trade agreement.
Opportunities for Indian Electronics Sector
India’s electronics sector stands to benefit significantly from the current trade landscape. With Indian electronics exports valued at nearly USD 14 billion, the U.S. tariffs on Chinese electronics make Indian products more competitive in the American market. Major global brands, including Apple, are likely to increase their production in India to avoid the higher costs associated with Chinese imports. This could lead to a surge in exports of finished electronic devices and components, such as batteries and circuit boards.
The demand for non-Chinese suppliers presents a unique opportunity for Indian electronics manufacturers to expand their operations and capture a larger share of the global market. Initiatives like the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes for electronics manufacturing can further enhance India’s competitiveness by reducing cost barriers for exports. By leveraging these strategic initiatives, India can position itself as a reliable supplier in the global electronics market.
Strategic Moves in Semiconductor Manufacturing
The U.S. has also excluded semiconductors from reciprocal tariffs, recognizing their critical role in national security and technological advancement. The semiconductor industry is vital for various sectors, and disruptions in this supply chain could have significant implications. The U.S. is actively promoting domestic semiconductor manufacturing through the CHIPS Act, which allocates $52 billion for local production. This move aims to bolster the U.S. semiconductor industry and reduce reliance on foreign suppliers.
With major chip manufacturers like Intel and TSMC investing in new facilities, the exemption from reciprocal tariffs supports this domestic growth strategy. The current global semiconductor supply chain is complex, with significant production concentrated in Taiwan and South Korea. Disrupting this network would be challenging, and relocating existing capacity would require substantial investment and time. Therefore, the U.S. strategy emphasizes strengthening domestic capabilities while maintaining essential partnerships with countries like India.
Future Prospects for U.S.-India Trade Relations
The temporary suspension of U.S. reciprocal tariffs aligns with India’s broader efforts to enhance trade relations with the United States. Both nations are actively working towards a Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA) aimed at doubling bilateral trade to $500 billion by 2030. This agreement could further solidify India’s position as a key player in global trade and manufacturing.
To capitalize on this opportunity, India must address existing challenges, improve market access to the U.S., and leverage initiatives like “Make in India.” By fostering strategic partnerships and collaborations with U.S. businesses, India can minimize reciprocal tariffs and drive sustained long-term export growth. The coming months will be crucial in shaping the future of global trade dynamics, and India’s proactive approach could enhance its role as a reliable global supplier.
Observer Voice is the one stop site for National, International news, Sports, Editor’s Choice, Art/culture contents, Quotes and much more. We also cover historical contents. Historical contents includes World History, Indian History, and what happened today. The website also covers Entertainment across the India and World.
Follow Us on Twitter, Instagram, Facebook, & LinkedIn

