Government Initiatives for Food Security and Nutrition
Food is a basic necessity for every individual. Ensuring that everyone has access to sufficient and nutritious food is vital for overall health and well-being. Recognizing this, the government has launched several innovative schemes aimed at improving food accessibility while maintaining high nutritional standards. These initiatives not only provide essential rations at fair prices but also focus on the nutritional needs of mothers and newborns. By promoting holistic health, these programs strive to ensure that every citizen has access to both food and proper nutrition.
Public Distribution System (PDS)
The Public Distribution System (PDS) is a crucial mechanism for managing food scarcity in India. It was established to distribute food grains at affordable prices to those in need. Over the years, PDS has evolved into a significant part of the government’s strategy for managing the food economy in the country. The system aims to ensure that essential food items reach the most vulnerable populations.
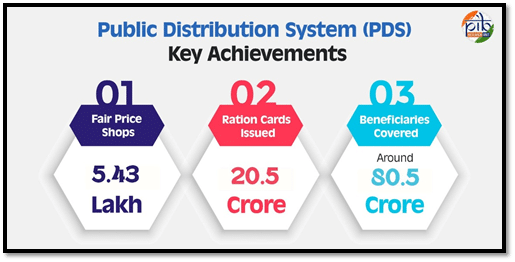
One of the key achievements of the PDS is the complete digitization of ration cards and beneficiaries’ data under the National Food Security Act (NFSA). This initiative has made information about approximately 20.5 crore ration cards, covering around 80.5 crore beneficiaries, accessible on transparency portals across states and union territories. Furthermore, more than 99.8% of ration cards have been linked to Aadhaar, ensuring that at least one member of each household is verified.
Additionally, about 99.6% of Fair Price Shops (FPSs) in the country are now automated with electronic Point of Sale (ePoS) devices. This automation has enhanced transparency and efficiency in the distribution of subsidized food grains. Moreover, over 97% of transactions related to food grain distribution are now recorded biometrically or Aadhaar-authenticated, further ensuring that the benefits reach the intended recipients. These advancements in the PDS have significantly improved food security for millions of people across the nation.
PM POSHAN Scheme
The PM POSHAN (POSHAN Shakti Nirman) Scheme, formerly known as the National Programme for Mid-Day Meal in Schools, was launched to enhance the nutritional status of school children. Approved for the period from 2021-22 to 2025-26, this initiative aims to improve school enrollment, attendance, and retention by providing nutritional support to primary school children. The program has expanded over the years, initially covering only primary classes and later including upper primary classes.
The financial outlay for the PM POSHAN Scheme is substantial, with the central government contributing ₹54,061.73 crores and state governments adding ₹31,733.17 crores. Additionally, the central government will bear an extra cost of about ₹45,000 crores for food grains, bringing the total budget for the scheme to ₹1,30,794.90 crores. This significant investment underscores the government’s commitment to improving the nutritional status of children in schools.
The budget allocated for the PM POSHAN Scheme has seen a steady increase over the years, rising from ₹6,539.52 crores in 2008-09 to ₹8,457.74 crores in 2023-24. This growth reflects the government’s recognition of the importance of nutrition in education and child development. By providing nutritious meals, the PM POSHAN Scheme not only addresses hunger but also promotes better learning outcomes for children across the country.
PM Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme (PMFME)
The PM Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises Scheme (PMFME) was launched to support the growth of micro food processing units in India. This scheme is operational from 2020-21 to 2025-26, with an outlay of ₹10,000 crores. The primary objective is to provide financial, technical, and business assistance to upgrade existing micro food processing enterprises and establish new units.
Since its inception, the PMFME Scheme has shown remarkable progress. The project cost under the scheme has increased significantly, from ₹390.99 crores in 2021-22 to ₹5,198.3 crores in 2023-24. This growth indicates a rising interest in the food processing sector and the potential for economic development in this area. Additionally, the number of food processing units has surged from 2,885 in 2021-22 to an impressive 54,730 in 2023-24.
The PMFME Scheme has also played a vital role in job creation. Employment generated through the scheme rose dramatically from 14,201 jobs in 2021-22 to 1,88,802 jobs in 2023-24. This increase not only supports the livelihoods of many individuals but also contributes to the overall economic development of the country. By formalizing micro food processing enterprises, the government aims to enhance the quality and safety of food products while boosting the local economy.
Observer Voice is the one stop site for National, International news, Sports, Editor’s Choice, Art/culture contents, Quotes and much more. We also cover historical contents. Historical contents includes World History, Indian History, and what happened today. The website also covers Entertainment across the India and World.

