India’s Investment Landscape: Recent Trends and Insights
India’s investment ecosystem has undergone remarkable changes in recent years. A recent report by the State Bank of India (SBI) sheds light on the trends in investment announcements, the private sector’s contributions, and the role of external commercial borrowings (ECBs) in corporate financing. This article explores these developments, highlighting the growth in investment activity, the status of corporate gross blocks, household savings, and the significance of ECBs in financing.
Growth in Investment Announcements
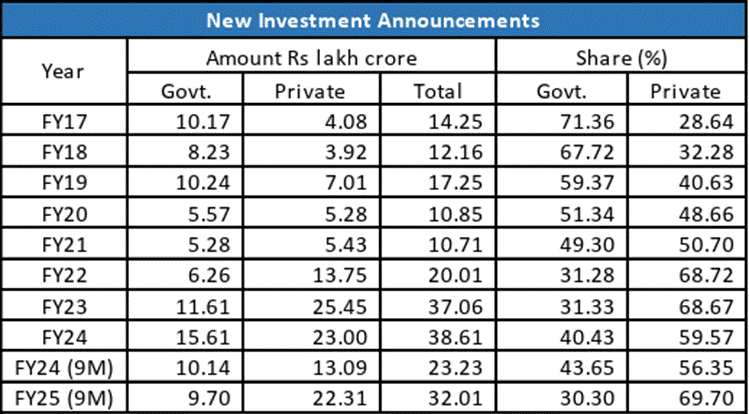
Investment activity in India has surged, driven primarily by the private sector. In the first nine months of the fiscal year 2025 (April-December 2024), total investment announcements reached an impressive ₹32.01 lakh crore. This figure represents a significant 39% increase from ₹23 lakh crore during the same period in the previous fiscal year (9MFY24). The private sector’s contribution has been substantial, accounting for nearly 70% of these announcements in 9MFY25, compared to 56% in FY24. This trend indicates a strong corporate confidence in the Indian economy and its growth potential.
The increase in investment announcements reflects a positive outlook among businesses. Companies are keen to expand their operations and invest in new projects. This growth is not just a short-term phenomenon; it signals a long-term commitment to enhancing India’s economic landscape. The robust investment climate is expected to create jobs, boost productivity, and foster innovation across various sectors.
Moreover, the rising trend in investment announcements is crucial for sustaining economic growth. It provides a foundation for infrastructure development, technological advancements, and overall economic resilience. As the private sector continues to play a pivotal role in driving investments, the government is also expected to support these initiatives through favorable policies and incentives.
Corporate Gross Block and Capital Expenditure
As of March 2024, the gross block of Indian corporates reached ₹106.50 lakh crore, a significant increase from ₹73.94 lakh crore in March 2020. This growth underscores the expanding capacity of Indian companies to invest in infrastructure and modernization. Over the past five years, an average of more than ₹8 lakh crore has been added annually to the corporate gross block, indicating a consistent trend of capital investment.
In addition to the gross block, capital work in progress stood at ₹13.63 lakh crore in March 2024. This figure highlights the ongoing development of projects across various sectors, including manufacturing, services, and infrastructure. The substantial capital work in progress suggests that companies are not only investing in new projects but are also committed to completing existing ones.
The increase in corporate gross block and capital expenditure is vital for economic growth. It enhances the productive capacity of the economy and contributes to job creation. As companies invest in new technologies and infrastructure, they can improve efficiency and competitiveness. This, in turn, can lead to higher economic output and improved living standards for the population.
Household Financial Savings and Investment Trends
Household Net Financial Savings (HNFS) in India improved to 5.3% of GDP in FY24, up from 5.0% in FY23. This increase indicates a growing propensity among households to save, which is essential for economic stability. Additionally, savings in physical assets rose from 12.9% of GDP in FY23 to 13.5% in FY24. This trend reflects a shift in household investment behavior, with more individuals opting for tangible assets.
Investment as a percentage of GDP has also seen positive developments in recent years. In FY23, government investment reached 4.1% of GDP, the highest level since FY12. Meanwhile, private corporate investment rose to 11.9% of GDP, marking its highest level since FY16. The share of private investment is projected to increase further to around 12.5% in FY24, indicating improved business sentiment.
The rise in household savings and investment as a percentage of GDP is crucial for sustaining economic growth. It provides a buffer against economic shocks and supports long-term investment in infrastructure and development projects. As households continue to save and invest, they contribute to the overall stability and resilience of the Indian economy.
The Role of External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs)
External Commercial Borrowings (ECBs) have become a vital source of funding for Indian corporates, facilitating capital expansion and modernization. As of September 2024, the total outstanding ECBs stood at $190.4 billion. Of this amount, the non-Rupee and non-FDI components accounted for approximately $154.9 billion. The private sector holds 63% of the total ECBs, while the public sector accounts for 37%.
The ECB pipeline remains strong, reflecting sustained demand for overseas funding. By November 2024, total ECB registrations reached $33.8 billion, with nearly half of the registrations aimed at importing capital goods, modernization, and local capital expenditure. This trend indicates that Indian companies are actively seeking international funding to support their growth initiatives.
Interest rates on ECBs have shown a declining trend, reducing borrowing costs for Indian companies. The overall cost of ECBs fell by 12 basis points year-over-year to 6.6% during April-November 2024. In November 2024, the cost further declined to 5.8%, a reduction of 71 basis points from the previous month. This decline in borrowing costs is beneficial for companies looking to finance their expansion plans.
Observer Voice is the one stop site for National, International news, Sports, Editor’s Choice, Art/culture contents, Quotes and much more. We also cover historical contents. Historical contents includes World History, Indian History, and what happened today. The website also covers Entertainment across the India and World.

