Household Consumption Expenditure Survey for 2022-23 and 2023-24
The National Statistics Office (NSO) has released its latest report, “Nutritional Intake in India,” based on the Household Consumption Expenditure Surveys (HCES) conducted from August 2022 to July 2024. This comprehensive study provides insights into the daily food consumption patterns of Indian households, detailing calorie, protein, and fat intake across various demographics. The findings reveal notable trends in nutritional intake, highlighting disparities between rural and urban populations and the impact of economic factors on dietary habits.
Overview of Nutritional Intake
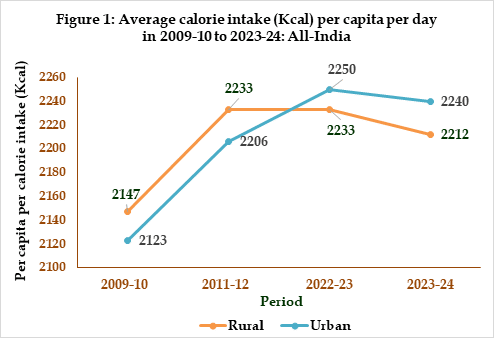
The report presents a detailed analysis of average daily per capita and per consumer unit intake of calories, protein, and fat for the years 2022-23 and 2023-24. In rural India, the average calorie intake was recorded at 2,233 Kcal in 2022-23 and slightly decreased to 2,212 Kcal in 2023-24. Conversely, urban areas showed a similar trend, with an average intake of 2,250 Kcal in 2022-23, dropping to 2,240 Kcal in the following year. This data indicates a consistent pattern in calorie consumption across both sectors, with variations observed among different states. The report also notes an increase in calorie intake among the lower fractile classes in both rural and urban settings, suggesting improvements in dietary access for economically disadvantaged groups.
Impact of Economic Factors on Nutritional Intake
The report highlights a significant correlation between Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE) and calorie intake. As the MPCE increases, so does the average calorie intake in both rural and urban areas. This trend underscores the importance of economic stability in improving nutritional outcomes. Furthermore, the report indicates a narrowing gap in calorie intake between the lowest and highest expenditure classes, reflecting a gradual improvement in dietary equality. This shift is crucial for policymakers and researchers aiming to address nutritional disparities across different segments of the population.
Trends in Nutritional Composition
The analysis of nutrient intake reveals that cereals remain the primary source of protein for both rural and urban populations, accounting for approximately 46-47% of protein intake in rural areas and about 39% in urban settings. However, there has been a notable decline in the share of protein derived from cereals over the years, with increases in the consumption of eggs, fish, meat, and other food categories. This shift indicates changing dietary preferences and a diversification of food sources among the Indian population. The report emphasizes the need for continued monitoring of these trends to ensure that nutritional policies align with evolving dietary habits.
Adjusted vs. Unadjusted Nutrient Intake
The report also discusses the differences between adjusted and unadjusted nutrient intake figures. Adjustments are made to account for food consumed by non-household members and meals purchased from the market. The findings indicate that adjusted nutrient figures are generally lower than unadjusted ones, reflecting a more accurate representation of household consumption. This distinction is vital for understanding true nutrient intake levels and for formulating effective nutritional policies. The report concludes by emphasizing the importance of comprehensive data collection in shaping future dietary guidelines and interventions aimed at improving the nutritional health of the Indian population.
Observer Voice is the one stop site for National, International news, Sports, Editor’s Choice, Art/culture contents, Quotes and much more. We also cover historical contents. Historical contents includes World History, Indian History, and what happened today. The website also covers Entertainment across the India and World.
Follow Us on Twitter, Instagram, Facebook, & LinkedIn

