New Optical Sensing Platform Developed for Cholesterol Detection
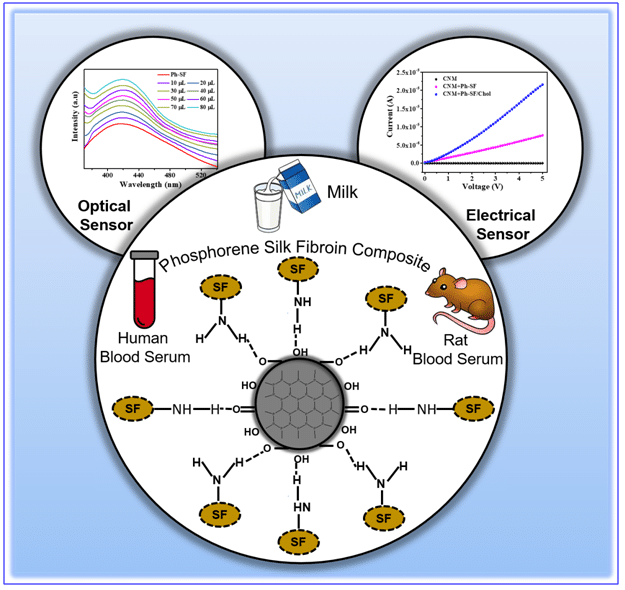
A groundbreaking optical sensing platform has been developed to detect cholesterol levels, offering a promising tool for early diagnosis of serious health conditions such as atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, and even cancer. This innovative technology, created by a team of researchers at the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST) in Guwahati, is designed to provide reliable point-of-care (POC) detection of cholesterol, which is crucial for personalized health monitoring. The device not only promises cost-effectiveness but also emphasizes eco-friendliness, making it a significant advancement in medical diagnostics.
Understanding Cholesterol and Its Health Implications
Cholesterol plays a vital role in human health, being produced by the liver and necessary for various bodily functions. It serves as a precursor for vitamin D, bile acids, and steroid hormones, and is essential for the structure of animal tissues, blood, and nerve cells. Cholesterol is transported through the bloodstream in two forms: low-density lipoprotein (LDL), often labeled as ‘bad’ cholesterol due to its tendency to accumulate in artery walls, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), known as ‘good’ cholesterol. Maintaining a balance between these two types is critical, as both high and low cholesterol levels can lead to severe health issues, including heart disease and hypertension. Excess cholesterol can result in atherosclerotic plaques, which obstruct blood flow and increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events.
Innovative Optical Sensing Technology
The optical sensing platform developed by the IASST team utilizes silk fiber functionalized with phosphorene quantum dots to detect cholesterol levels. This cutting-edge technology allows for the detection of cholesterol in trace amounts, even below the recommended range, making it an effective tool for routine health monitoring. The project is spearheaded by a team that includes Prof. Neelotpal Sen Sarma, Dr. Asis Bala, and Ms. Nasrin Sultana, who have integrated silk fiber into a cellulose nitrate membrane to create an efficient electrical sensing platform. This innovative approach not only enhances sensitivity but also ensures that the device generates no electronic waste, addressing environmental concerns associated with traditional medical devices.
Real-World Applications and Research Findings
The sensors developed through this research have demonstrated high sensitivity and selectivity for cholesterol detection. They have been tested in various real-world media, including human blood serum, experimental rat blood serum, and milk, showing consistent performance across different samples. This versatility highlights the potential for widespread application in clinical settings. The findings of this research have been published in the journal “Nanoscale,” under the Royal Society of Chemistry, further validating the significance of this advancement in cholesterol detection technology. With its eco-friendly design and high efficiency, this optical sensing platform could revolutionize how cholesterol levels are monitored, ultimately contributing to better health outcomes for patients at risk of serious diseases.
Observer Voice is the one stop site for National, International news, Sports, Editor’s Choice, Art/culture contents, Quotes and much more. We also cover historical contents. Historical contents includes World History, Indian History, and what happened today. The website also covers Entertainment across the India and World.

