Smallest Galaxy Discovered Challenges Cosmic Theories
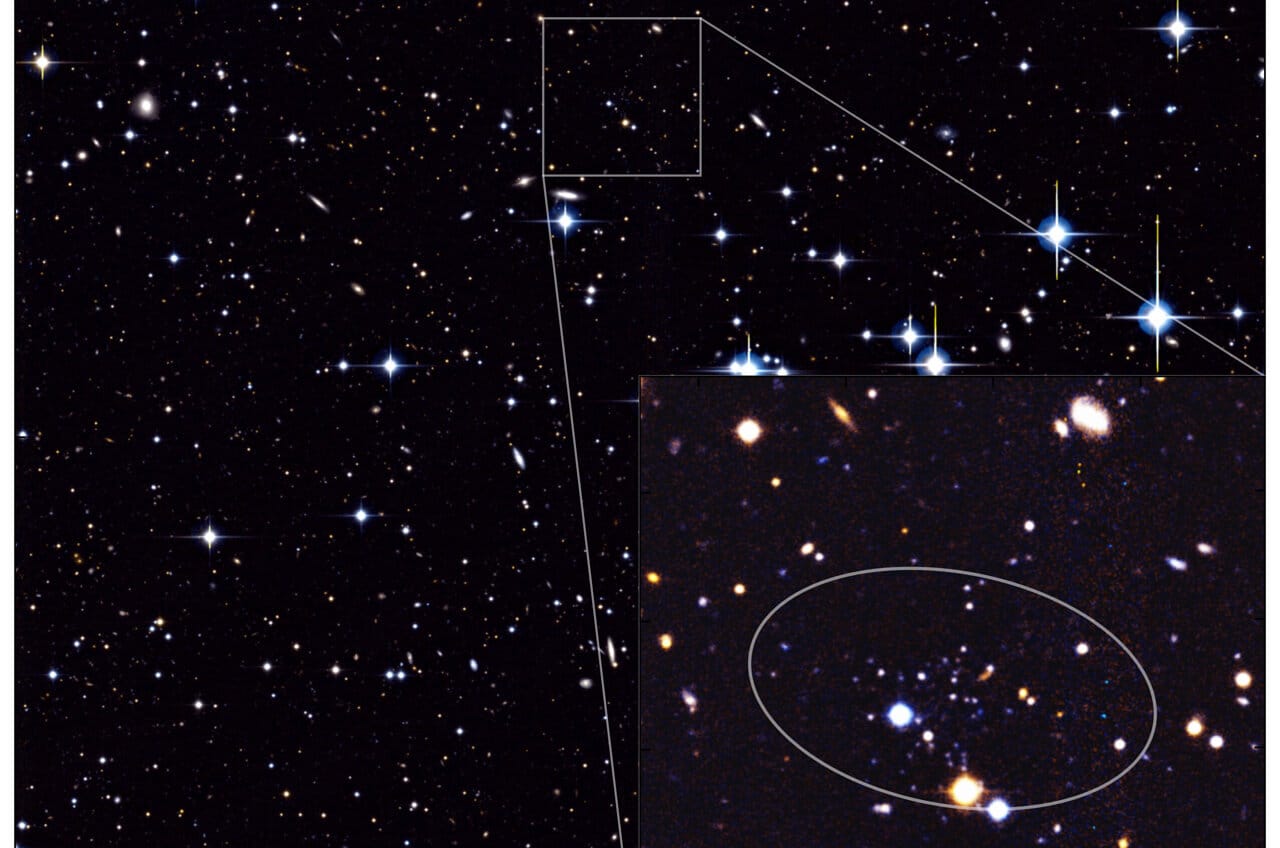
Astronomers have made a groundbreaking discovery by identifying the smallest and faintest galaxy ever observed, located around 3 million light-years from Earth. Named Andromeda XXXV, this galaxy defies existing theories on galaxy formation, which suggested that such tiny galaxies would have been obliterated in the early universe’s extreme conditions. Researchers believe that understanding Andromeda XXXV could significantly alter our comprehension of cosmic evolution and the survival of small galaxies.
Characteristics of Andromeda XXXV
Andromeda XXXV stands out as a remarkably small galaxy, measuring approximately 1,000 light-years across at its longest axis. This discovery was confirmed through data collected from various astronomical surveys and observations made with the Hubble Space Telescope. Eric Bell, a professor at the University of Michigan, characterized Andromeda XXXV as “a fully functional galaxy, but about a millionth the size of the Milky Way.” Despite its diminutive size, scientists are intrigued by its ability to maintain the conditions necessary for star formation, a feat not commonly seen in such small galaxies.
The Challenge of Detecting Dwarf Galaxies
Dwarf galaxies are prevalent in the universe, yet they pose significant challenges for detection due to their faintness. While the Milky Way has several known satellite galaxies, identifying similar structures around Andromeda has proven difficult. Previous discoveries in the Andromeda region were larger and brighter, fitting existing models of galaxy formation. However, Andromeda XXXV is unique due to its extended period of star formation. Lead researcher Marcos Arias noted that some galaxies of similar size in Andromeda continued forming stars up to 6 billion years ago, while most of the Milky Way’s satellite galaxies ceased star formation around 10 billion years ago.
Implications for Galaxy Formation Theories
The existence of Andromeda XXXV raises important questions about why it survived the harsh conditions that likely disrupted other small galaxies. Bell described the early universe as “like a vat of boiling oil,” a time when galaxies were expected to lose the gas essential for star formation. The survival of Andromeda XXXV suggests that existing theories regarding galaxy formation and evolution may require significant reevaluation. Ongoing research and future space missions are anticipated to shed more light on how galaxies like Andromeda XXXV managed to endure despite the challenging cosmic environment.
Observer Voice is the one stop site for National, International news, Sports, Editor’s Choice, Art/culture contents, Quotes and much more. We also cover historical contents. Historical contents includes World History, Indian History, and what happened today. The website also covers Entertainment across the India and World.

